Overview of Incision and Drainage Procedure
Incision and drainage (I&D) is a widely used procedure in primary and acute care settings to treat abscesses, involving a minor surgical intervention to drain pus and promote healing.
1.1 Importance of the Procedure in Primary and Acute Care Settings
Incision and drainage is a critical skill in primary and acute care, essential for treating abscesses to relieve pain, reduce infection risk, and promote healing. It is frequently performed in emergency departments and outpatient clinics, making it a cornerstone procedure for managing soft tissue infections effectively.
1.2 Brief Description of the I&D Method
Incision and drainage involves making a small surgical cut to drain pus from an abscess, typically under local anesthesia. The procedure allows pus to exit, relieving pain and promoting healing. It is a minor surgical intervention often performed in outpatient or emergency settings to address soft tissue infections effectively.
Step-by-Step Guide to the Incision and Drainage Procedure
The procedure involves preparing materials, patient verification, making an incision, draining pus, and applying dressings. Each step is performed under sterile conditions to ensure proper healing.
2.1 Preparing the Necessary Materials and Equipment
Essential materials include sterile gloves, antiseptic solution, scalpels, forceps, gauze, and appropriate dressings. Gather all supplies beforehand to ensure efficiency and maintain asepsis during the procedure.
2.2 Patient Identification and Verification
Patient identification and verification are crucial steps to ensure the correct procedure is performed on the right individual. This involves confirming the patient’s identity using medical records or ID bands and verifying the procedure details, including the site of the abscess. Accurate verification prevents mix-ups and ensures safety, maintaining trust and minimizing potential complications.
2.3 Making the Incision and Draining the Abscess
Making the incision involves creating a small, strategic cut in the skin over the abscess to allow pus drainage. Local anesthesia is often used to minimize pain. The procedure may include flushing the area with saline to remove residual pus. Proper technique ensures complete drainage, reducing the risk of recurrence. A sterile field is maintained to prevent infection during the process.
2.4 Use of Special Dressings for Wound Healing
Special dressings, such as gauze or antimicrobial dressings, are applied after incision and drainage to promote wound healing. These dressings help absorb drainage, maintain a moist environment, and protect the wound from infection. Proper dressing selection and application are crucial for optimal healing. Follow-up care includes regular dressing changes, as guided by healthcare providers, to monitor healing progress and prevent complications.
Indications for Incision and Drainage
Indications for I&D include large, fluctuant abscesses, persistent symptoms despite antibiotics, or significant tissue damage. It is essential for relieving pain and preventing infection spread.
3.1 Diagnosing Skin Abscesses and Fluctuance
Diagnosing skin abscesses involves clinical examination, identifying tenderness, swelling, and fluctuance. Fluctuance indicates fluid collection, confirming abscess presence. Imaging may aid complex cases. Accurate diagnosis is crucial for timely intervention, ensuring proper treatment and preventing complications.
3.2 When Antibiotics Alone Are Insufficient
Antibiotics alone may fail to resolve deep, large, or complex abscesses. In such cases, incision and drainage is essential to physically remove pus, reducing bacterial load and promoting healing. Persistent infection or inadequate response to antibiotics necessitates surgical intervention to prevent complications and ensure recovery.
Post-Procedure Care and Patient Instructions
Proper wound care includes regular dressing changes, keeping the site clean, and monitoring for signs of infection. Patients should follow specific instructions to ensure optimal healing and recovery.
4.1 Wound Dressing Changes and Frequency
Wound dressings should be changed daily for the first two days post-surgery, then as needed. Patients must keep the site clean and dry to promote healing and prevent infection. Follow specific instructions from healthcare providers regarding dressing frequency and type to ensure proper wound care and recovery.
4.2 Keeping the Incision Site Clean and Dry
Keeping the incision site clean and dry is crucial to prevent infection and promote healing. Gently clean the area with mild soap and water, avoiding harsh scrubbing. Pat dry thoroughly after cleaning or bathing. Avoid submerging the wound in water until fully healed. Do not apply lotions or ointments unless directed by a healthcare provider. Adhere to these practices to ensure proper recovery.
Complications and Risks Associated with I&D
Complications include infection, abscess recurrence, and delayed healing. Proper sterilization and technique reduce risks, ensuring patient safety and effective recovery from the procedure.
5.1 Possible Infections and Rare Complications
While rare, complications from I&D may include infections, abscess recurrence, or spreading of pus to deeper tissues. Proper sterilization and hygiene are crucial to prevent these issues. Infections like MRSA can arise if not managed correctly, emphasizing the need for meticulous technique and post-procedure care to ensure patient safety and optimal recovery outcomes.
5.2 Importance of Proper Sterilization and Hygiene
Proper sterilization and hygiene are critical in I&D to prevent infections and ensure a safe procedure. Using sterile equipment and maintaining a clean environment minimizes the risk of complications. Adherence to hand hygiene guidelines and post-procedure care protocols helps prevent the spread of pathogens, promoting successful wound healing and reducing the likelihood of rare but serious infections such as MRSA.
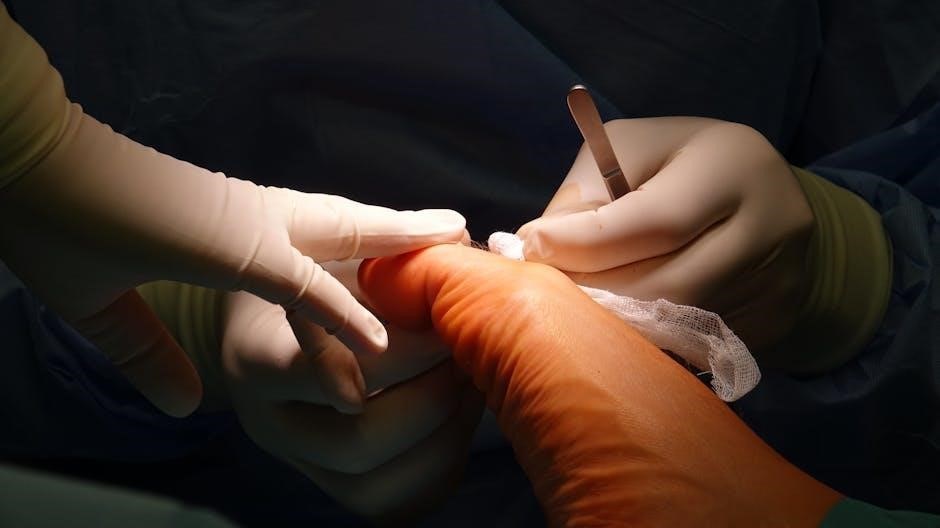
Clinical Guidelines and Best Practices
Clinical guidelines emphasize standardized surgical and anesthetic procedures for I&D, ensuring routine cultures and appropriate antibiotics usage to optimize patient outcomes and minimize complications.
6.1 Standardized Surgical and Anesthetic Procedures
Standardized surgical and anesthetic protocols ensure consistency and safety in I&D procedures. Local anesthesia is commonly used to minimize pain, followed by a precise incision to drain pus. The cavity is flushed with saline, and appropriate dressings are applied to promote healing and prevent infection, adhering to established clinical guidelines for optimal outcomes.
Routine cultures and antibiotics are not always necessary after a successful I&D procedure. However, in cases of complex infections or patient-specific factors, cultures can help identify causative organisms, guiding targeted antibiotic therapy. Antibiotics may be reserved for cases where systemic infection or spreading cellulitis is present, ensuring judicious use and minimizing resistance risks.
Special Considerations in Specific Cases
6.2 Role of Routine Cultures and Antibiotics
Routine cultures and antibiotics are not always necessary after a successful I&D procedure. However, in cases of complex infections or patient-specific factors, cultures can help identify causative organisms, guiding targeted antibiotic therapy. Antibiotics may be reserved for cases where systemic infection or spreading cellulitis is present, ensuring judicious use and minimizing resistance risks.
7.1 Draining Abscesses in Sensitive Areas
Draining abscesses in sensitive areas, such as the face, neck, or perirectal region, requires extra caution and precision to avoid complications. Local anesthesia is often used to minimize discomfort. A small, carefully placed incision is made to drain pus while preserving surrounding tissue. Special consideration is given to post-procedure care, including gentle dressings and follow-up to ensure proper healing and prevent infection.
7.2 Surgical Assessment for Complex Abscesses
Complex abscesses, particularly those in challenging locations or with multiple compartments, often require surgical assessment. A thorough evaluation by a specialist determines the need for advanced techniques, such as debridement or drainage under anesthesia. Imaging studies may guide the approach, ensuring complete removal of infected tissue and promoting optimal healing outcomes while minimizing recurrence risk.
Patient Recovery and Return to Normal Activities
Most patients can resume normal activities within a week, though healing time varies. Activity restrictions depend on the procedure’s complexity, with follow-up care essential for full recovery.
8.1 Expected Healing Time and Activity Restrictions
Healing typically takes 1-2 weeks, with most patients returning to normal activities within 7 days. Activity restrictions may include avoiding strenuous tasks and keeping the site dry to prevent infection. Follow-up care is crucial to monitor progress and ensure proper wound healing, reducing the risk of complications and promoting a speedy recovery.
8.2 Follow-Up Care and Monitoring
Follow-up care involves regular wound checks and dressing changes to ensure proper healing. Patients should monitor for signs of infection, such as redness, swelling, or increased pain. They should contact their healthcare provider if symptoms persist or worsen. Adherence to post-procedure instructions is crucial for preventing complications and promoting a smooth recovery.
Documentation and Reporting
Accurate documentation of the procedure, including details of the incision, drainage, and patient response, is essential for legal and continuity of care purposes.
9.1 Recording Procedure Details and Patient Response
Accurate documentation of the I&D procedure is crucial, including the size and location of the incision, amount of drainage, and any complications. Patient response, such as pain or discomfort, should also be noted. Detailed records ensure legal compliance and facilitate continuity of care, providing a clear reference for future treatment decisions and patient monitoring.
9.2 Importance of Accurate Medical Records
Accurate medical records are vital for legal compliance, continuity of care, and patient safety. They provide a clear timeline of treatment, ensuring consistency among healthcare providers. Detailed documentation also protects against legal disputes and improves patient outcomes by enabling precise tracking of progress and response to the I&D procedure.
Incision and drainage is a highly effective procedure for treating abscesses. Adherence to proper technique and post-procedure care is crucial for optimal patient outcomes and recovery.
10.1 Summary of Key Points
Incision and drainage is a critical procedure for treating abscesses, promoting healing, and preventing complications. Proper technique, sterilization, and patient care are essential. Post-procedure wound management and follow-up care ensure optimal recovery; Adherence to clinical guidelines and best practices minimizes risks and improves outcomes, making I&D a fundamental skill in primary and acute care settings.
10.2 Emphasis on Proper Technique and Patient Care
Proper technique in incision and drainage is vital for successful outcomes, ensuring minimal complications and promoting faster healing. Sterilization, precise incision, and gentle drainage are critical. Patient care includes post-procedure monitoring, wound dressing, and clear instructions for home care. Attention to detail and adherence to clinical guidelines enhance safety and efficacy, prioritizing patient well-being and optimal recovery.